Flow measurements of large rivers by ADCP
Principle of the ADCP
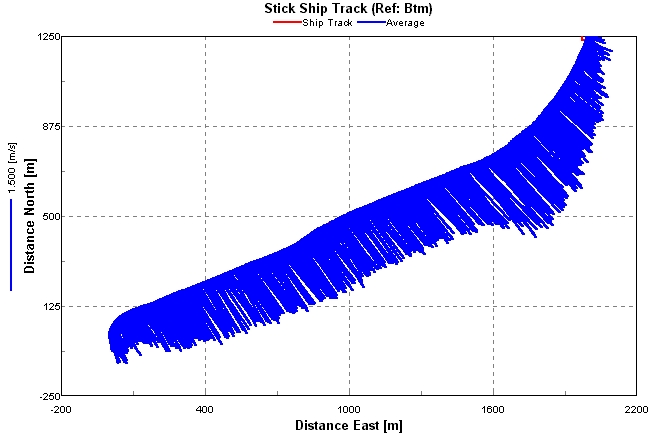
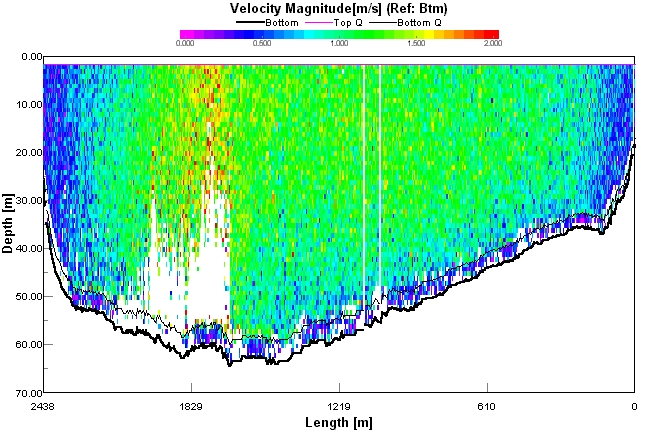
To improve the quality of hydrological measurement, particularly at hydrometric stations influenced by downstream hydraulic control, the HYBAM programme acquired a 300 KHz Doppler Current meter – ADCP in 1994. This equipment uses the frequency variation between the transmitted signal and the signal reflected by the suspended particles to calculate the water velocity and direction (RDI, 1989). The calculation is automatically performed in real time by the TRANSECT software, installed on a laptop computer. When the ADCP is correctly installed in a traditional Amazonian boat, the software calculates the speed and unit flow in cells of variable size, during the boat’s movement from one bank to the other. When measuring, the boat’s speed may not exceed 5 knots, or about 10 km.h-1. On arrival, the cumulative value of the unit flows corresponds to the flow rate of the volumetric section. The size of each cell depends on the configuration used (cell height), the programming of the ADCP signal transmission (number of pings per minute), as well as the boat’s speed (cell width). In a section more than 2 km wide like Óbidos, the interval between 2 pings is generally 1 to 3 seconds, which generates 600 to 1800 vertical sections. Finally, each of these verticals is cut into cells 1 to 2 m high. The positioning of each vertical is done in relation to the bottom echo, which is considered stable. Thus, the flow rate can be measured, regardless of the vessel’s trajectory, the direction of the current, and the geometry of the section. A visualization module allows the real-time monitoring of the gauging operation by ADCP, with the generation of graphs such as the boat’s trajectory (figure 3), or the speed profile in the measured section (figure 4).
|
|
|
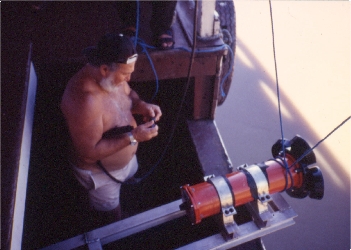
| Figure 1: 300 KHz ADCP on Amazonian boat. | Figure 2: Gauging by ADCP on an Amazonian boat, Rio Negro, Brazil. |
Operational protocol
Based on observations and in situ work on the reproducibility of flow measurements during the first HYBAM field missions to the Brazilian Amazon (Guyot et al., 1994, 1995), an operational protocol was developed. This protocol recommends 4 successive gauges of the same section to obtain a representative flow value, but also to evaluate the possible drift of the bottom reference during floods (Guimarães et al., 1997 ; Callède et al., 2000 ; Filizola et al., in press). The coordinates of the starting point and end point of each gauge are determined by GPS. The distance to the shoreline is estimated, usually using a clinometer. The ADCP, which has been used in all HYBAM field missions for flow measurement, has enabled the creation of a database on the hydrodynamic parameters of many gauged sections. This information has been compiled in the HYBAM geo-referenced database.
|
|
| Figure 3: ADCP gauging: vessel trajectory and distribution of surface velocity vectors Rio Amazonas at Obidos, Brazil, 16/12/2003. |
|
|
| Figure 4: ADCP Gauging: Cross profile, and velocity distribution in the section Rio Amazonas in Obidos, Brazil, 16/12/2003. |
Bibliographical references
Callède J., Kosuth P., Guyot J.L., Guimarães V. 2000. Discharge determination by acoustic doppler current profilers (ADCP) : a moving bottom error correction method and its application on the river Amazon at Obidos. Hydrological Sciences Journal, 45(6) : 911-924.
Filizola N. 2003. Transfert sédimentaire actuel par les fleuves amazoniens. Thèse de doctorat, Université P. Sabatier, Toulouse. 292 p.
Filizola N., Guimarães V., Guyot J.L. (submitted). Water discharge measurements at the Amazon river with the acoustic doppler current profiler. Hydrological Processes.
Guimarães V., Guyot J.L., Filizola N., Oliveira E. 1997. O uso do ADCP (correntômetro de perfilagem acústico por efeito Doppler) para medição de vazão e estimativa do fluxo de sedimentos nos grandes rios da bacia amazônica, 545-552. In XII Simpósio Brasileiro de Recursos Hídricos, Anais 1, ABRH, Vítoria, Nov. de 1997.
Guyot J.L., Conceição S., Guimarães V., dos Santos J.B., Longuinhos R. 1995. Medição de vazão com ADCP – Primeiros resultados na bacia Amazônica. A Água em Revista, 3(4) : 26-30. CPRM, Rio de Janeiro.
Guyot J.L., Guimarães V., Santos J.B., Longuinhos R., Conceição S. da. 1994. Primeira campanha de medições de vazão com ADCP no Rio Amazonas. Publ. HiBAm, Brasília, 29 p.